
Diodes
 Diodes are
electric components which force current to flow in only
one direction. They are formed by connecting p-type and
n-type semiconductors as shown to the right. When current
flows from the p-type to the n-type material, the
positive holes and the negative electrons are forced into
close contact at the boundary. At the boundary, the
electrons fill the holes across the boundary while the
terminals supply new holes and electrons. Thus, in the forward
bias case a continual current flows. In the
reverse bias case, the charge carriers are pulled apart.
There is no longer an easy way for electrons to tunnel
through the barrier as there are no longer many empty
holes waiting on the opposite side. Diodes are
electric components which force current to flow in only
one direction. They are formed by connecting p-type and
n-type semiconductors as shown to the right. When current
flows from the p-type to the n-type material, the
positive holes and the negative electrons are forced into
close contact at the boundary. At the boundary, the
electrons fill the holes across the boundary while the
terminals supply new holes and electrons. Thus, in the forward
bias case a continual current flows. In the
reverse bias case, the charge carriers are pulled apart.
There is no longer an easy way for electrons to tunnel
through the barrier as there are no longer many empty
holes waiting on the opposite side.
The circuit-diagram
representation of a diode is 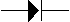 with the arrow representing the
direction current is allowed to flow. with the arrow representing the
direction current is allowed to flow.
Semiconductor
devices' index
|