1. Which force, electromagnetic(E), gravitational(G), weak nuclear(WN) or strong nuclear(SN), is primarily responsible for the following actions:
|
falling from a tree. G |
pressurizing a balloon. E |
|
orbiting of planets. G |
dissolving sugar in water. E |
|
exploding of a firecracker. E |
coloring of paints. E |
|
fusion of Deuterium in the sun. SN |
melting of an ice cube. E |
|
ebbing of the tide. G |
ringing of a bell. E |
|
burning of a candle. E |
breathing the air. E |
|
heating a TV dinner in a microwave oven. E |
smelling a flower. E |
|
cycling of ATP & ADP in the body. E |
flying a jet plane. E and G |
|
air-conditioning a room. E |
freezing of ice cream. E |
|
firing of a gun. E |
decay of the isotope Carbon-14 WN |
|
recording on an audio tape. E |
fertilizing of a egg. E |
2. Tension forces are generated when stretching an object. They exist at the ends of the object and the interior of object.
3. Compression forces are generated when squeezing an object. They exist at the ends of the object and also interior of the object.
4. The new spacing of the atoms is ![]() , with (#)
, with (#)![]() atoms within, and (#)
atoms within, and (#)![]() atoms beyond the old length. (slightly more accurate method on next page)
atoms beyond the old length. (slightly more accurate method on next page)
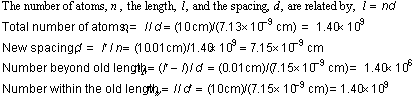
5. The nucleus occupies (fraction) ![]() of the volume in an atom.
of the volume in an atom.
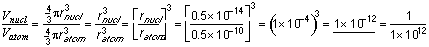
6. An elastic object will return to normal length when the forces distorting it are removed.
7. Which of the following in normal use do not behave elastically?
|
beach sand, |
a guitar string, |
a pencil, |
a concrete walkway, |
|
the wing of an airplane, |
a frozen ice cube, |
ice cream, |
an accordion, |
|
a banana |
a feather pillow |
a candy cane |
an eyelash |
8. True or false: when the forces acting on my body are balanced I don’t feel them.
9. True or false: the forces acting on the atoms in an undistorted object are balanced.
10. To make a neutral object have a positive charge I must remove electrons.
11. Maxwell determined that light combined the effects of the electric and magnetic forces.
12. The speed of light will remain the same if I run toward the source of the light. The speed of a vehicle on earth does depend on the speed of the observer. It was A. Einstein who explained both phenomena by the same theory.
13. A new theory can replace an old theory if it:
1. predicts phenomena incorrectly described by old theory
2. explains why the old (incomplete) theory correctly predicted other phenomena. (the new theory must correctly predict these phenomena as well)
14. Chemical reactions move electrons from the + pole of a battery to the – pole.
15. There are two atoms of oxygen in an oxygen molecule. An oxygen molecule must split to burn hydrogen gas (H2) and form water (H2O): O2+2H2 ––> H2O + H2O
Back to Homework List