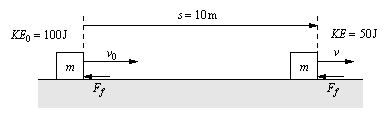

5. The change in the kinetic energy of the mass is,
6. The missing energy was converted to heat energy in the table and the mass.
7. The non-conservative force that is affecting its speed is called friction.
8. The non-conservative force does an amount of work on the mass,
9. The mass travels 10m, therefore the average force acting on it was
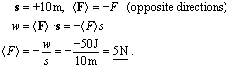
10. (New questions) The force(s), electromagnetic(E), gravitational(G), weak nuclear(WN) or strong nuclear(SN), is(are) primarily responsible for the following:
| color of a green leaf. E | screech of a tire on a road. E |
| scatter of neutrons off a nucleus. SN | hardness of a diamond. E |
| period of Haley's comet (76 years). G | smell of brie cheese. E |
| beta decay producing a 3.5 MeV electron WN | sound of a beating heart. E |
| boiling of water E | decay of the Roman Empire. E |
| shape of a salt crystal. E | fall of a thrown baseball. G |
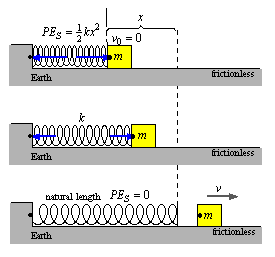
11. Acting on the small mass in the horizontal direction the initial force is ,
12. Acting on the small mass in the vertical direction the net force is zero
13. The spring stores an initial potential energy is
14. When the mass leaves the spring the speed is
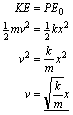
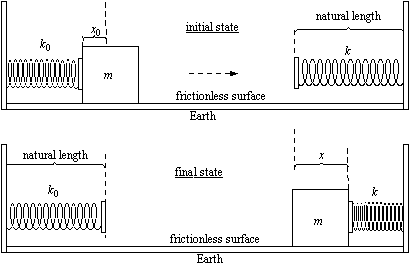
15. A spring compressed by a distance, x0, with spring constant, k0, gives, without loss, its stored energy to a mass that slides on a frictionless table attached to the earth as shown above. The mass then hits a second spring with spring constant, k , and compresses it by a distance, x , again without loosing energy. In terms of the spring constants, the ratio of the compressions.
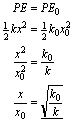
True or False (ignoring air friction):
T 15. The work done to raise a mass sitting on the floor to one sitting on a table without changing direction does not depend on how fast it is done.
F 16. Work is a vector because it can be either positive or negative.
F 17. A mass thrown upward has no forces acting on it at the highest point.
18. Which pair, below, are both considered non-conservative forces?
(a) gravitational and ideal spring forces
(b) gravitational and human forces
(c) ideal spring and human forces
(d) frictional and human forces
(e) elastic and frictional forces
Chapter 10, Problems 1-6
A mass is slowly raised from the floor to a table top by the force
of a human hand (FH).
1. The other force acting on the mass during this motion is gravity .
2. The signs of the work done by the two forces is opposite
3. The net force acting on the mass during its motion upward is zero .
4. The a net amount of work done by the net force on the mass is zero .
5. At the floor the kinetic energy of the mass is, KE0= zero , and at the table, KE = zero.
6. The net work done by both forces on the mass is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the mass.