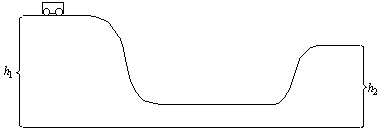

7. The speed, v , of the cart when it has reached the top of the hill with a height h1 is:
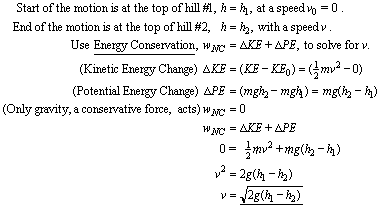
The person weighs 500 N and puts 1500 J of PE into the trampoline in one bounce. Lowest height is , h = h0 = 0, max. height, h = h2.
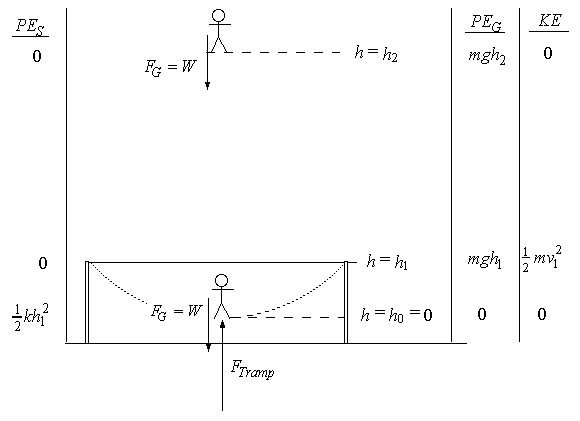
8. Gravity, FG = mg, downward, always acts on the person. The trampoline acts upward on the person and has a magnitude greater than mg at the bottom where the person's speed is increased from zero.
9. Net force direction at the high point is down, and at the low point is up, on the person.
10. Trampoline energy is transferred to the person. The person gets to a height h2 = 3 m .
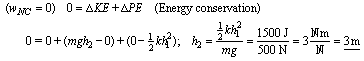
11. Trampoline spring constant is 100 N/cm (104 N/m). The person's lowest distance below the surface of the trampoline is the value of h1 = 0.55 m
12. What is the speed, v , of the person when leaving the surface of the trampoline?
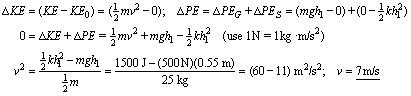
13. What is the highest point the person gets above the surface of the trampoline?
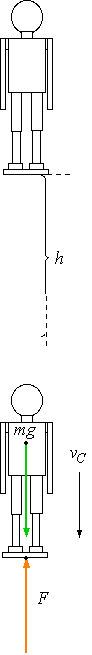
14. The human, at the initial height, has potential energy =
17. The two forces acting on the human when the speed reaches vC:
18. The net force, FNet , on the human being when the speed reaches vC is zero (speed has a constant value of vC)
After reaching vC, the human falls an additional distance x.
19. The change in potential energy, DPEG (final - initial), of the human over the distance, x is