1. Which force(s), electromagnetic(E), gravitational(G), weak nuclear(WN) or strong nuclear(SN), is(are) primarily responsible for the following (100% correct for credit):
| photosynthesis. E | friction. E |
| emission of neutrons SN | lubrication with oil E |
| orbiting. G | lightning . E |
| decay n –> proton + e + n. WN | thunder. E |
| decay of tooth. E | pain. E |
| shape of a snowflake. E | formation of diamonds G & E |
3. An object will compress when two inward forces of magnitude, F, act on it.
4. FGon a 1 kg mass is 10N. The 1 kg mass applies a force 10N on the Earth.
5. FG is 100N on a mass on the earth. The mass is 10 kg and its weight is 100 N .
6. The gravitational force (use m in your answers) is: mg
in the hand of the thrower,
mg when moving upward, : mg at the highest
point, : mg on the way down, and : mg when
it hits the ground. The weight (does or does not)
change in the motion.
7. M contains 10 masses, m. FG acting on the large mass is 10 mg, on the earth is 10 mg.
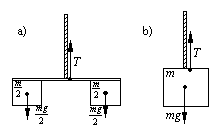
8. The weight vectors are drawn. T is a) mg, and
b) mg. (use m in your answers)


9. Rope spring constant k .The stretch x = mg/k
10. The compression in each leg is 175 N (using g=10m/s^2 or 172 N (using g=9.8m/s^2).
11. ![]() . The weight
is 800 N (or 784 N with g=9.8).
. The weight
is 800 N (or 784 N with g=9.8).
12. The force vectors (FG) are drawn on the fig.
13. Weight is a) m b) 2m c) mg d) 2 mg e) mg/2
14. Tension vectors, TB, in bar are drawn on fig.
TB = a) m b) 2m c) mg
d) 2 mg e) mg/2
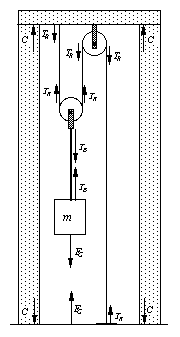
15. Tension vectors, TR, are drawn on fig.
TR = a) mg b) mg/2 c) 2 mg
d) 3 mg e) mg/3
16. Force, F, pulling down on the roof is
F = a) mg b) mg/2 c) 2mg/3 d) 3mg/2
e) mg/3
17. Forces, C, in walls are drawn on fig. The value
C = a) mg b) mg/4 c) 4mg/3 d) 3mg/4
e) mg/2
18. True or false questions (all correct for credit) refer to the previous
problems 13-17.
T F: The forces acting on the earth (from problems 13, 15 and
17) are in balance.
T F: The forces acting on the roof (from problems 16 and 17) are in balance.
T F: The forces acting on the mass (from problems 13 and 14) are in balance.
T F: The forces acting on pulley (#1) (from problems 14 and 15) are in balance.
T F: A rope tension (from problem 15) half the weight of the
mass keeps it at rest.

A rope, pulleys on a pole, and a spring (all massless) attached to the ground, support a mass m as shown. The spring is stretched, x, by the weight of the mass.
19. The gravitational force vectors are drawn on fig.
FG = mg .
20. Tension force vectors are drawn on the fig.
TR, = mg.
The relationship is FG = TR
The relationship between TR and m is TR
= mg
21. Tension force vectors in spring are drawn on fig
The relationship between TR and T is TR
= T
The relationship between T and m is T = mg
22. Compression forces vectors in the pole are drawn on the fig.
The relationship between C and T is C = 2T
The relationship between C and m is C = 2mg
23. The spring stretch is x = 2mg/k.
24. The force vectors are , T = +T ,C =
–C , and FG=mg , acting on
the earth (+ is up)
The vector sum is T + C + FG +T + (–C)
+ FG = mg +(–2mg) + mg = 0 .
The forces acting on the earth ( are or are not)
balanced.
Back to Homework List