| color of TV screen. E | thinking about life. E |
| exposure of photo film. E | measuring speed by radar. E |
| clotting of blood to a scab. E | measuring speed by laser. E |
| decay of a neutron to proton+e+n WN | location of the rings of Saturn. G |
| microwave heating . E | bending of light by a prism. E |
| spoiling of milk. E | floating of helium-filled balloon . E & G |
3. A mass weighs 100 N on the planet Kongo (gKongo
= 2.5 N/kg). What is its weight on the Earth? gKongo
= 2.5 N/kg
a) 4 N b) 400 N c) 2.5 N
d) 4000 N e) 250 N
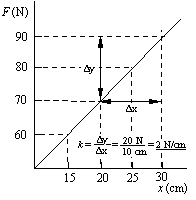
5. Assume this spring continues to behave as shown for smaller values
of the stretch down to x = 0. Substitute a value for F and
x at one point on the line into the equation of the line, F =
kx + F0, to determine, F0, the force when
the spring just begins to stretch.
a) 0 N b) 5 N c) 10 N
d) 20 N e) 30 N
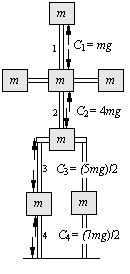
6. Draw on the figure to the left the compression vectors (arbitrary
length) acting on the masses in the vertical bones #1 to #4, and label
them, C1 to C4, respectively.
See picture at left.
7. What is the magnitude of C1, the compression
in bone #1?
a) 1.0 mg b) 2.5 mg
c) 3.0 mg d) 3.5 mg e)
4.0 mg
8. What is the magnitude of C2, the compression
in bone #2?
a) 1.0 mg b) 2.5 mg
c) 3.0 mg d) 3.5 mg e)
4.0 mg
9. What is the magnitude of C4, the compression
in bone #4?
a) 1.0 mg b) 2.5 mg
c) 3.0 mg d) 3.5 mg
e) 4.0 mg
10. What is the magnitude of the net gravitational force acting on earth
from these masses?
a) 1.0 mg b) 3.0 mg
c) 5.0 mg d) 7.0 mg
e) 9.0 mg

A diver (W = mg) is at the end of a diving board L meters long. The board is tied to the ground at the rear with a post (with tension T) and rests on a point support, a pivot point (with compression C), 1/10 of the length from the left end.
11. Draw force vectors, CD (diver), C
(pivot), and tension, T (rear), acting on the board.
See above picture.
12. How far is the diver from the pivot? a) 1.0 L, b) 0.9 L, c) 0.1 L, d) 1.1 L, e) 9.0 L
13. What are the torque vectors about the pivot generated by
(+ is clockwise)
the diver tD
= +mg(9L/10) , and at rear tR
= T(L/10)