Transformers
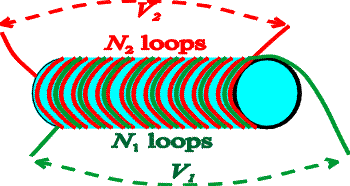
Transformers are used to change the voltage of an AC voltage source. This can be done by winding two sets of coils around the same core as shown below.

Every loop of wire has the
same flux through it, and hence the same rate of change in flux, and hence
produces the same voltage. The voltage across each coil is therefore proportional to the number
of turns in it, so the voltages are related by
V2 = (N2 / N1) V1
If the green loop is hooked to a power supply
with voltage V1, the red wires will serve
as a power supply with an increased voltage
V2 if there are more red than green
turns around the core.
No power is gained or lost in the transformer (we neglect the
resistance of the wires), so the power going out of the transformer equals
the power going in. Hence
V1 I1 = V2 I2
. If the voltage increases, the current
decreases; in general
Note that transformers depend on changes in flux, so they work only for AC, not DC. The ease in changing voltages with transformers is the reason that AC is used for the distribution of electric power.