Examples for atomic physics
Example #1
Problem:
True or False:
a.) An electron in the ground state of a Hydrogen atom has zero orbital angular momentum.
b.) An electron in the ground state of a Hydrogen atom has zero spin angular momentum.
c.) An electron in the ground state of a Hydrogen atom has zero kinetic energy.
d.) An electron in the ground state of a Hydrogen atom has zero probability of being at the origin.
e.) An electron in the n=2 level of Hydrogen will emit visible light when it decays to the ground state.
T,F,F,F,F
Example #2
Problem:
a.) What is the energy of a photon emitted as an electron moves from the n = 5 to the n = 2 level in hydrogen?
Solution:
The energy of each level goes as (13.6 eV)/n2. The difference between the n = 5 and n = 2 values is the photon's energy.
2.9 eV
b.) What is the wavelength of such a photon?
Solution:
Change the energy to Joules, then use E
= hf to get the frequency. Then get the wavelength. OR use the
formula: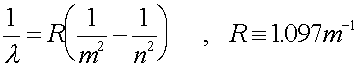
686 nm
c.) What is the energy of a photon in the same transition is carbon (Z=6)?
Solution:
The energy scales as Z2, so multiply the answer in part a by 36.
103 eV
Example #2
Problem:
a.) How many electrons are in an atom specified by 1s2,2s2,2p6,3s2,3p4?
Solution:
Count up the numbers in the superscripts.
16
b.) Write the spectroscopic notation for a neutral gold (Au) atom? See periodic table.
Solution:
See that a gold atom should have 79 electrons by looking at the periodic table. Then count up:
1s2,2s2,2p6,3s2,3p6,3d10,4s2,4p6,4d10,4f14,5s2,5p6,5d10,5f1