Student Name:
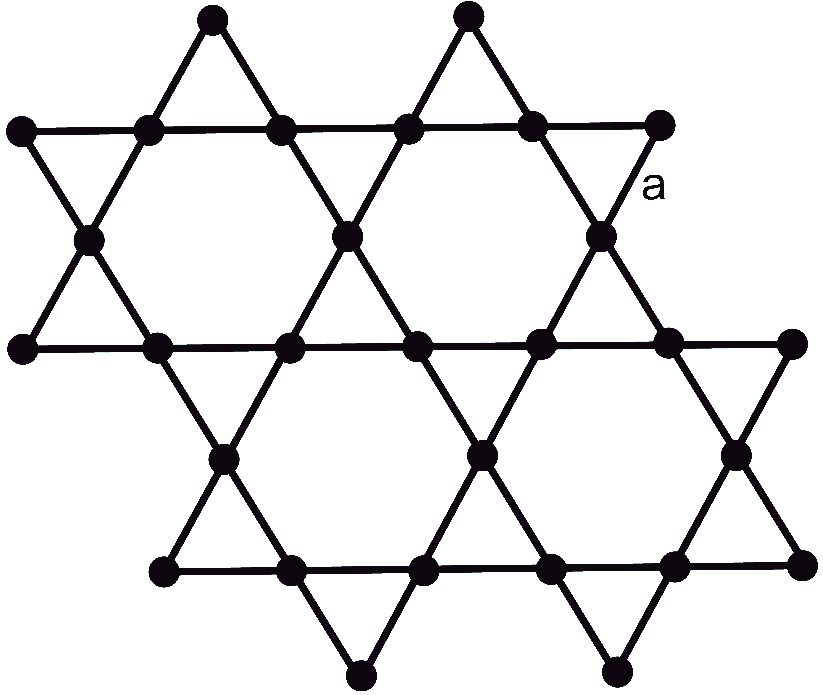
1. Below is a sketch of the Kagome lattice, where all the atoms are chemically equivalent. The nearest neighbor separation is a.

(a) (3 pt.) How many atoms are there in the primitive unit cell and what is its area?
(b) (6 pt.) Determine the direct Bravais lattice vectors and the reciprocal lattice vectors.
(c) (3 pt.) Sketch the reciprocal lattice. Show the first and the second Brillouin zone.
(d) (3 pt.) Determine the irreducible part of the first Brillouin zone. What fraction of the full Brillouin zone does it occupy?
2. (7 pt.) The lattice contains N unit cells, where N is a very large number. How many states are there in the first Brillouin zone? How many in the second? Justify your answer.
3. Discuss the symmetry of the lattice:
(a) (1 pt.) Does the lattice have inversion symmetry? If so, indicate the inversion center in the figure.
(b) (1 pt.) Are there any mirror planes? If so, how many?
(c) (1 pt.) Is the system invariant under rotations? If so, indicate the rotation axis for n-fold rotations.
(d) (1 pt. bonus) Locate other rotation axes for m-fold rotations, with m different from n.
4. Consider a Kagome lattice, where the nearest neighbor distance a=0.2 nm. An X-ray is incident along the direction indicated in the figure, under 60o from the normal. A detector measures the intensity of the X-rays scattered specularly in the plane of the lattice under 60o from the normal, as shown in the figure.
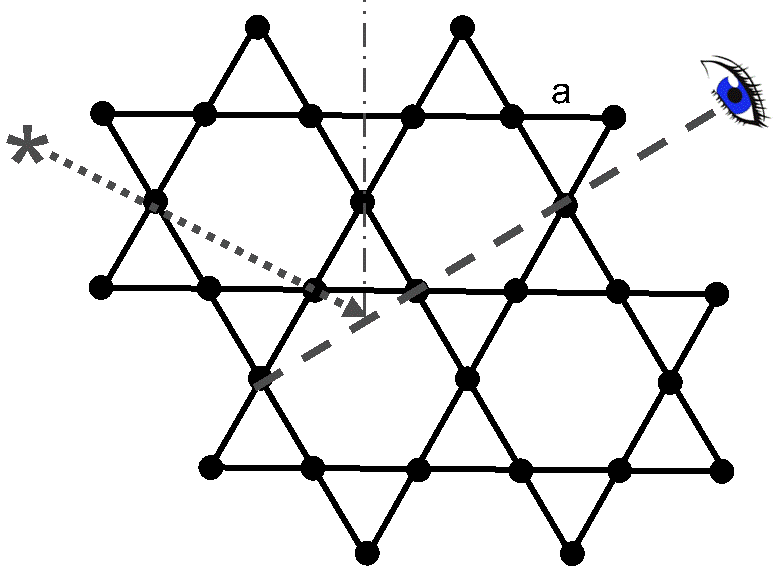
(a) (3 pt.) Which is the longest wavelength λ of the X-rays that may yield constructive interference?
(b) (2 pt.) Give one more wavelength λ', which may yield constructive interference under these conditions.
(c) (1 pt.) Can you imagine a reason, why the above conditions might result in a destructive interference after all? Explain.
5. (5 pt.) The elastic Kagome lattice is suspended in space. What is the total number of phonon modes of each of the following type: longitudinal acoustic, transverse acoustic, longitudinal optical, and transverse optical?