Interactive examples: solutions
Basic examples
Single atom
Pair of atoms
Row of atoms
Interactive examples
1D crystal builder
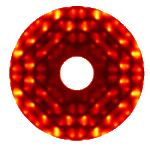
Polygons of atoms
Different atoms
Ewald sphere
Units
Interference
Goto
Contents
- Example 1:
1D crystal builder:
Playing with the
parameters generating the scattering from a row of atoms should
have shown you:
- As you increase the number of atoms, the main peaks get sharper and the number of maxima between them increases ..
- The distance of the atoms and the peaks in the scattering pattern behave in a reciprocal way: as you move the atoms further apart, the diffraction peaks come closer together and vice versa ..
- For the scattering of electrons as well as neutron scattering of atoms, all diffraction peaks have the same intensity, whereas X-ray scattering from atoms shows decreasing intensities as you go out in q. The reason for this is the fact that atoms are for X-rays an extended object whereas electrons in case of X-rays and all atoms in case of neutron scattering can be regarded as points.
- Example 2: Poylgon of atoms: The main point this exercise should have made is that the rotation symmetry in real space in preserved in the diffraction pattern. However, the scattering pattern shows in addition a center of inversion. For example the pattern for the triangle n=3 shows a 6-fold axis. Values n=1,2,3,4 and 6 are the only ones that give a diffraction pattern that shows translational periodicity. Indeed one can show that only those rotation axes are compatible with three dimensional translational periodicity found in crystals.
- Example 3: Different atoms: The obvious difference between neutron and X-ray scattering is the fact that the neutron scattering intensity for a single atom is constant in reciprocal space whereas X-ray scattering decreases with increasing Q. For X-rays the intensity at the origin is given by the number of electrons of the element squares. Neutron intensities on the other hand have no (although there is an overall trend) systematic behavior as one goes through the periodic table.