Diffuse scattering: Transversal waves
Diffuse scattering
Thermal I
Thermal II
Occupational I
Occupational II
Longitudinal waves
Transversal waves
Short range order
Stacking faults
Interactive examples
Displacement waves
Short range order
Stacking faults
Goto
Contents
wave vector [100] wave length 27A 5.2 unit cells oscillation [010] amplitude 0.5A 0.1 unit cells |
The left image shows a part of the crystal, 30*30 unit cells were used for the calculation. The right image shows one quadrant of reciprocal space.
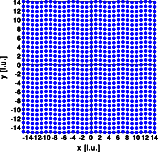
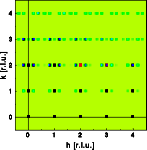
The satellite vector is 0.19 0 0, parallel to the wave vector in real space. Its absolute value is inversely proportional to the wave length. The intensity of the satellite reflections depends on the amplitude of the displacement. Contrary to the last example, now the satellites around the h00 reflections are systematically extinct. Here the term h ( u - < u > ) equals zero and no deviation from the averaged structure can be observed. Imagine the structure projected onto the 100 line. This projection is identical to that of a undisturbed crystal and accordingly the h00 reflections are identical.